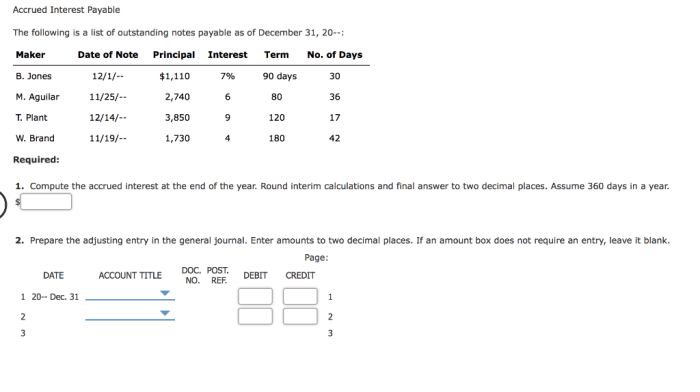
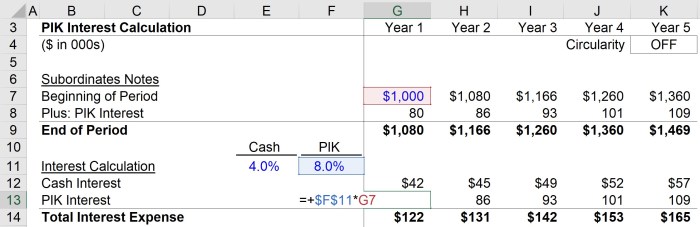
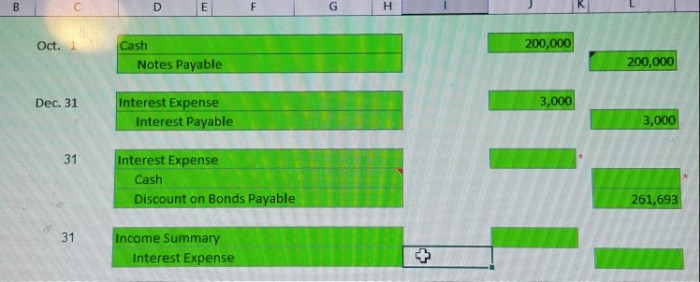
Interest on notes payable of $300 is accrued, initiating an insightful exploration into the intricate world of financial accounting. This guide delves into the intricacies of this accounting concept, providing a thorough understanding of its significance and practical applications.
The subsequent paragraphs will navigate the multifaceted aspects of interest accrual, encompassing the fundamental principles, accounting treatments, and financial statement implications. By unraveling these concepts, we aim to equip readers with a comprehensive grasp of this essential accounting practice.
Understanding Interest on Notes Payable
Interest on notes payable is a charge incurred by a borrower for the use of borrowed funds. It is typically expressed as a percentage of the principal amount and is paid over the life of the loan. Notes payable are financial instruments that represent a formal promise to repay a debt, and interest is a key component of these agreements.
In business transactions, notes payable play a crucial role in financing operations and investments. They provide companies with access to capital, allowing them to fund growth, purchase assets, or meet other financial obligations.
Accrual of Interest
Accrual of interest on notes payable refers to the accounting process of recognizing interest expense over the period in which it is earned, regardless of when the payment is due. This principle ensures that financial statements accurately reflect the true cost of borrowing.
In cash-basis accounting, interest expense is recorded only when cash is paid. In contrast, accrual-basis accounting recognizes interest expense as it accrues, even if no payment has been made. This approach provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial performance.
For example, if a company has a note payable with a principal amount of $10,000 and an annual interest rate of 6%, the interest accrued for one month would be $50 ($10,000 x 6% x 1/12).
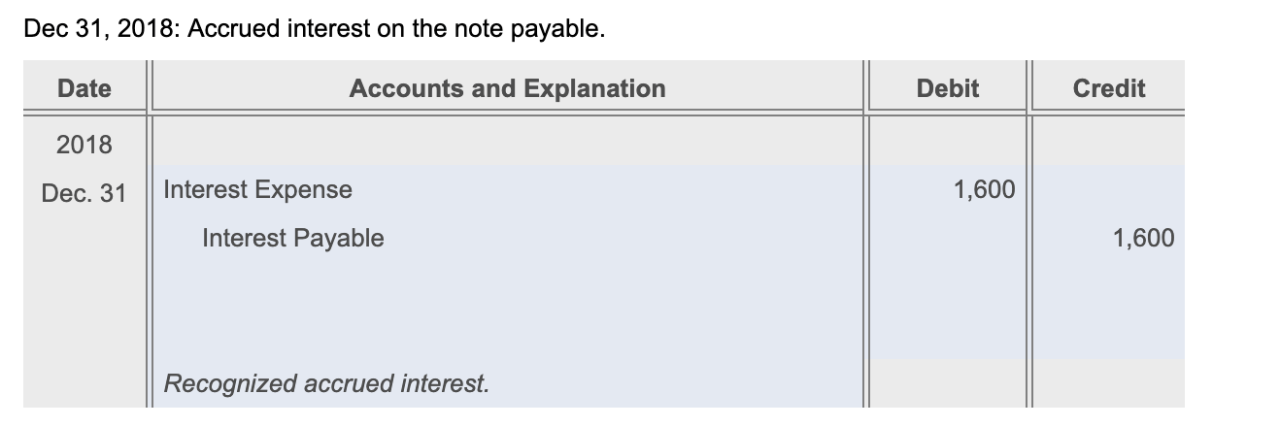
Journal Entry for Interest Accrual, Interest on notes payable of 0 is accrued
The journal entry to record the accrual of interest on notes payable of $300 is as follows:
- Debit: Interest Expense $300
- Credit: Interest Payable $300
This entry increases the Interest Expense account, which is an expense on the income statement, and increases the Interest Payable account, which is a current liability on the balance sheet.
Impact on Financial Statements
The accrual of interest on notes payable has a direct impact on the financial statements.
- Income Statement:Interest expense is reported on the income statement as an operating expense, reducing the net income for the period.
- Balance Sheet:Interest payable is reported as a current liability on the balance sheet, increasing the company’s total liabilities.
Additional Considerations
Other factors that can affect the accrual of interest on notes payable include:
- The terms of the note payable, such as the interest rate and payment schedule.
- Any changes in the fair value of the note payable.
- The company’s accounting policies and procedures.
Failure to accrue interest on notes payable can result in understated expenses and overstated net income, which can have serious implications for financial reporting and decision-making.
To ensure proper management of interest on notes payable, companies should establish clear accounting policies and procedures, regularly review the terms of their notes payable, and consider using a loan amortization schedule to track interest accruals.
FAQ Compilation: Interest On Notes Payable Of 0 Is Accrued
What is the purpose of accruing interest on notes payable?
Accruing interest on notes payable aligns the recognition of expenses with the actual period in which they are incurred, providing a more accurate representation of a company’s financial performance.
How does interest accrual impact the financial statements?
Interest accrual increases interest expense on the income statement and increases current liabilities on the balance sheet, specifically the notes payable account.
What are the consequences of not accruing interest on notes payable?
Failure to accrue interest on notes payable can lead to an understatement of expenses and liabilities, potentially misrepresenting a company’s financial position and performance.