The human body an orientation chapter 1 answer key – The Human Body: An Orientation – Chapter 1 Answer Key unlocks the secrets of the human body, providing a comprehensive guide to its intricate systems and functions. This chapter lays the foundation for a deeper understanding of our physical selves, exploring the skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems.
Through a captivating narrative, this answer key unravels the mysteries of the human body, revealing the interplay between its various components and their essential roles in maintaining life and well-being.
Introduction
The human body is a complex and fascinating organism. It is composed of trillions of cells, all working together to perform the functions necessary for life. The human body is divided into several systems, each of which has its own specific functions.
These systems include the skeletal system, muscular system, nervous system, endocrine system, cardiovascular system, respiratory system, digestive system, urinary system, and reproductive system.
Studying the human body is important for several reasons. First, it helps us to understand how our bodies work. This knowledge can help us to make informed decisions about our health and well-being. Second, studying the human body can help us to diagnose and treat diseases.
By understanding how the body works, we can develop new and more effective treatments for a variety of diseases.
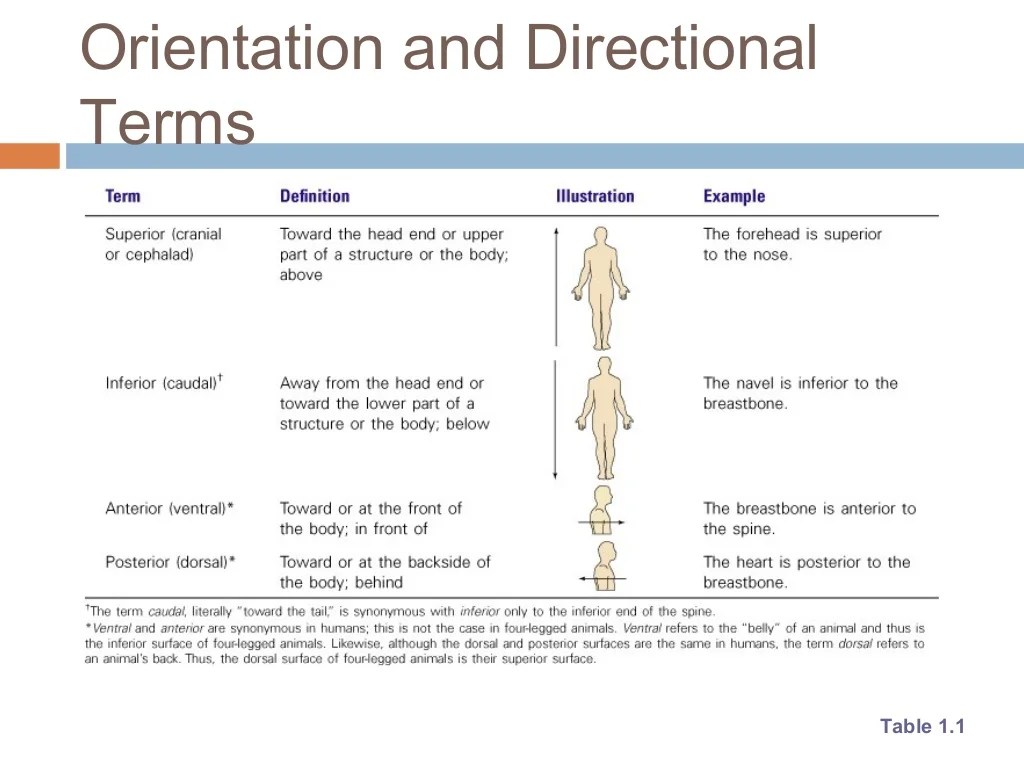
The basic structure of the human body is relatively simple. The body is made up of a head, neck, trunk, and limbs. The head contains the brain, which is the control center of the body. The neck connects the head to the trunk.
The trunk contains the heart, lungs, and other vital organs. The limbs include the arms and legs.
Skeletal System

The skeletal system is responsible for supporting the body, protecting the organs, and allowing for movement. The skeletal system is made up of bones, which are hard, mineralized tissues. Bones are connected to each other by joints, which allow for movement.
The skeletal system also produces red blood cells, which are essential for carrying oxygen throughout the body.
The structure of bones is complex. Bones are made up of a hard outer layer called the cortex and a softer inner layer called the medulla. The medulla contains red bone marrow, which is where red blood cells are produced.
Bones are also covered by a thin layer of tissue called the periosteum. The periosteum contains blood vessels and nerves that nourish the bone.
There are three main types of joints in the body: synovial joints, cartilaginous joints, and fibrous joints. Synovial joints are the most common type of joint. They are found in the knees, elbows, and shoulders. Synovial joints are lined with a thin layer of synovial fluid, which reduces friction and allows for smooth movement.
Cartilaginous joints are found in the spine and pelvis. Cartilaginous joints are connected by cartilage, which is a tough, flexible tissue. Fibrous joints are found in the skull and teeth. Fibrous joints are connected by ligaments, which are strong bands of tissue.
Muscular System
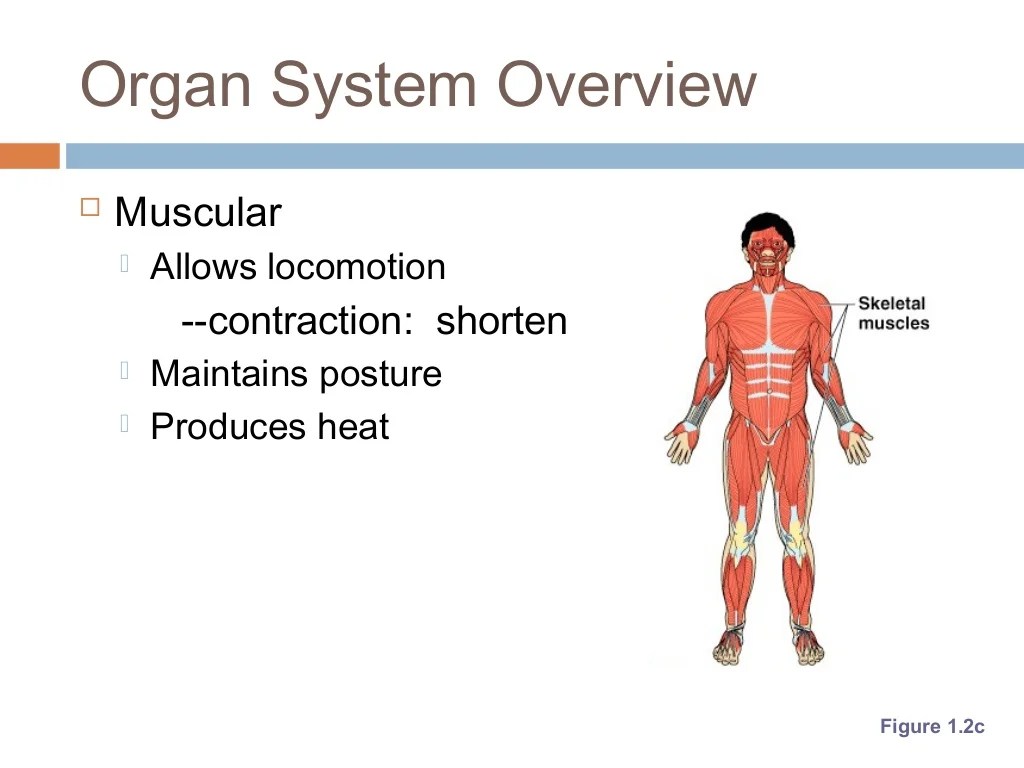
The muscular system is responsible for movement. The muscular system is made up of muscles, which are specialized tissues that can contract and relax. Muscles are attached to bones by tendons, which are tough bands of tissue. When a muscle contracts, it pulls on the tendon, which in turn pulls on the bone.
This causes the bone to move.
There are three main types of muscles in the body: skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, and cardiac muscles. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones and are responsible for voluntary movement. Smooth muscles are found in the walls of organs and blood vessels.
Smooth muscles are responsible for involuntary movement, such as the movement of food through the digestive system. Cardiac muscles are found in the heart. Cardiac muscles are responsible for the pumping action of the heart.
The structure of muscles is complex. Muscles are made up of bundles of muscle fibers. Muscle fibers are long, thin cells that contain myofibrils. Myofibrils are made up of actin and myosin filaments. When a muscle contracts, the actin and myosin filaments slide past each other, causing the muscle to shorten.
Nervous System
The nervous system is responsible for controlling the body’s activities. The nervous system is made up of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. The brain is the control center of the body. It receives information from the senses and sends signals to the muscles and organs.
The spinal cord is a long, thin bundle of nerves that runs from the brain to the rest of the body. The spinal cord carries messages between the brain and the rest of the body.
The nervous system is divided into two main parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is made up of the nerves that run from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body.
The brain is the most complex organ in the body. The brain is divided into two hemispheres: the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere. The left hemisphere is responsible for logical thinking, language, and mathematics. The right hemisphere is responsible for creativity, imagination, and emotions.
Endocrine System: The Human Body An Orientation Chapter 1 Answer Key
The endocrine system is responsible for regulating the body’s activities. The endocrine system is made up of glands, which are organs that produce hormones. Hormones are chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream and target specific cells. Hormones control a wide range of bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
The endocrine system is made up of several glands, including the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and pancreas. The pituitary gland is the master gland of the endocrine system. It produces hormones that control the other glands in the endocrine system.
Hormones are essential for life. They control a wide range of bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Without hormones, the body would not be able to function properly.
FAQ Guide
What is the purpose of the skeletal system?
The skeletal system provides support, protection, and movement for the body.
How many bones are there in the human body?
There are 206 bones in the adult human body.
What is the function of the nervous system?
The nervous system controls and coordinates all bodily functions, including movement, sensation, and thought.
What is the largest organ in the human body?
The skin is the largest organ in the human body.
What is the function of the circulatory system?
The circulatory system transports blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells and removing waste products.