Correctly label the following components of the kidney – In the realm of human anatomy, the kidneys stand as remarkable organs responsible for maintaining the delicate balance of our internal environment. Correctly identifying and understanding the intricate components of the kidney is crucial for unraveling its vital role in filtration, electrolyte regulation, and overall health.
This comprehensive guide will meticulously guide you through the structural and functional intricacies of the kidney, empowering you with a profound understanding of its essential components.
Nephron Components
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney, responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine. It consists of several distinct components:
Glomerulus
The glomerulus is a network of tiny blood vessels located at the beginning of the nephron. It is responsible for filtering waste products from the blood into the Bowman’s capsule, which surrounds the glomerulus.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
The proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) is the first part of the nephron after the glomerulus. It is responsible for reabsorbing essential nutrients, such as glucose, amino acids, and vitamins, from the filtrate.
Loop of Henle
The loop of Henle is a U-shaped structure that descends deep into the renal medulla and then ascends back up. It plays a crucial role in urine concentration by creating a gradient of osmolarity in the medulla.
Distal Convoluted Tubule
The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is the final part of the nephron before the collecting duct. It is responsible for fine-tuning the composition of the filtrate by reabsorbing or secreting ions and water.
Collecting Duct
The collecting duct is a system of ducts that collect urine from multiple nephrons and transport it to the renal pelvis. It is responsible for regulating the final composition of urine by reabsorbing or secreting water and ions.
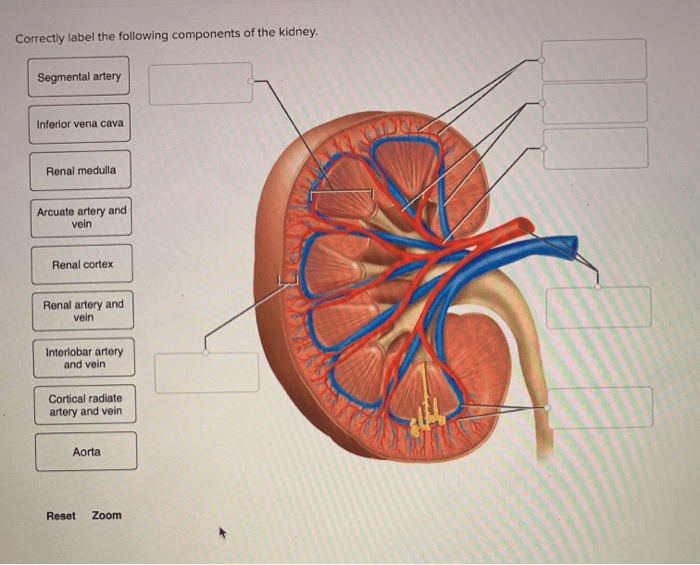
Renal Blood Vessels
The renal blood vessels are responsible for supplying blood to the kidneys and filtering waste products.
Renal Artery
The renal artery is the main blood vessel that supplies blood to the kidneys. It branches into smaller arteries within the kidney.
Renal Vein
The renal vein is the main blood vessel that drains blood from the kidneys. It carries waste products to the inferior vena cava.
Peritubular Capillaries
Peritubular capillaries are small blood vessels that surround the tubules of the nephron. They allow for the exchange of nutrients and waste products between the blood and the tubules.
Vasa Recta, Correctly label the following components of the kidney
Vasa recta are specialized blood vessels that descend deep into the renal medulla alongside the loop of Henle. They help maintain the osmolarity gradient in the medulla by exchanging ions and water with the surrounding tissue.
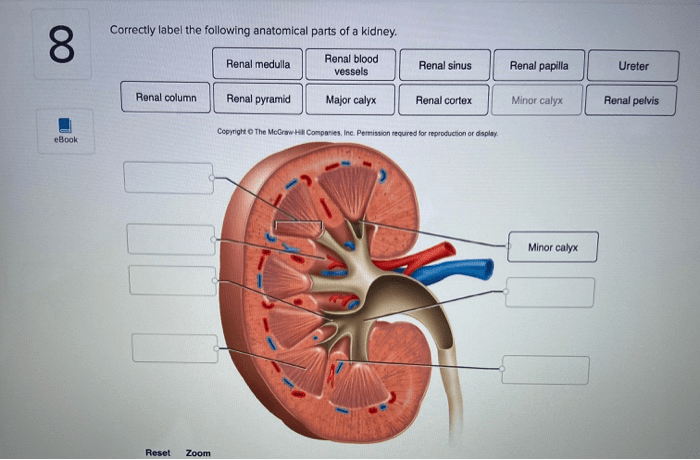
Renal Pelvis and Ureter
The renal pelvis is the funnel-shaped structure that collects urine from the collecting ducts.
Ureter
The ureter is a muscular tube that transports urine from the renal pelvis to the urinary bladder. It does this through peristalsis, a wave-like contraction of the muscle walls.
Renal Nerves and Lymphatics
The kidneys are innervated by both sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves.
Sympathetic Nerves
Sympathetic nerves stimulate vasoconstriction, which reduces blood flow to the kidneys.
Parasympathetic Nerves
Parasympathetic nerves stimulate vasodilation, which increases blood flow to the kidneys.
Lymphatic Drainage
The kidneys are drained by a network of lymphatic vessels that collect fluid and waste products from the kidney tissue.
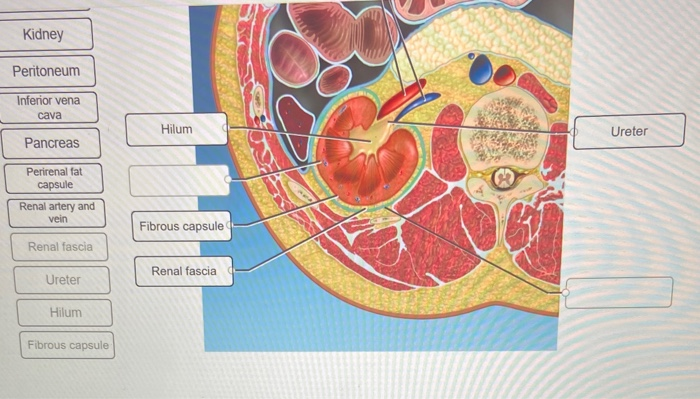
Renal Capsule and Adipose Tissue
The renal capsule is a thin layer of connective tissue that surrounds the kidney.
Perirenal Adipose Tissue
Perirenal adipose tissue is a layer of fat that surrounds the kidneys and provides protection and insulation.
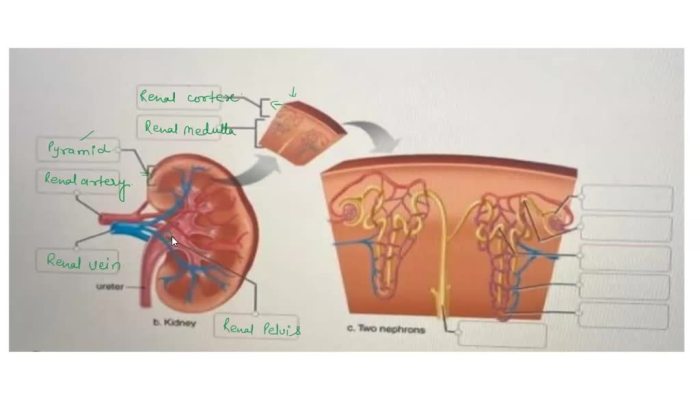
Histology of the Kidney: Correctly Label The Following Components Of The Kidney
The kidney has a distinct histological structure that can be divided into two main regions: the cortex and the medulla.
Renal Cortex
The renal cortex is the outer region of the kidney and contains the glomeruli, PCTs, and DCTs.
Renal Medulla
The renal medulla is the inner region of the kidney and contains the loops of Henle and collecting ducts.
Clarifying Questions
What is the primary function of the glomerulus?
The glomerulus is responsible for filtering waste products, excess water, and electrolytes from the blood, forming the initial filtrate that will eventually become urine.
What is the role of the proximal convoluted tubule?
The proximal convoluted tubule reabsorbs essential nutrients, water, and ions from the filtrate, actively transporting them back into the bloodstream.
How does the loop of Henle contribute to urine concentration?
The loop of Henle creates a concentration gradient in the kidney medulla, allowing for the reabsorption of water and the excretion of concentrated urine.