As the process of photosynthesis graphic organizer takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with authority, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. Delving into the intricacies of photosynthesis, this comprehensive guide unravels the fundamental concepts, reactions, and environmental factors that govern this vital process.
From the absorption of light energy to the intricate dance of enzymes, the process of photosynthesis is meticulously dissected, providing a clear understanding of its significance for plants, other organisms, and the global ecosystem. Accompanying this textual exposition is a meticulously designed graphic organizer, serving as a visual aid that reinforces the concepts and enhances comprehension.
Photosynthesis Overview: Process Of Photosynthesis Graphic Organizer
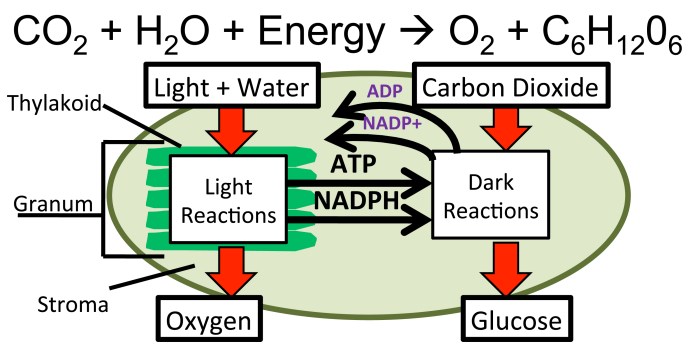
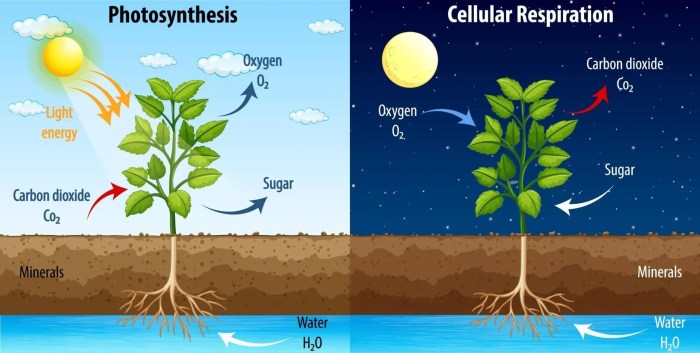
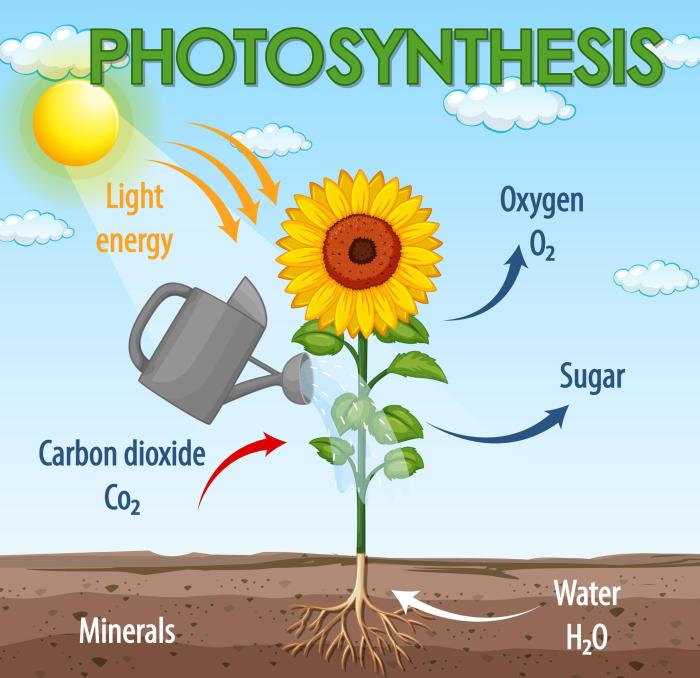
Photosynthesis is a fundamental process that converts light energy into chemical energy, producing oxygen and carbohydrates. It is performed by plants, algae, and certain bacteria, and forms the basis of the food chain and oxygen production on Earth.
Plants absorb sunlight through pigments, primarily chlorophyll, which then initiates a series of chemical reactions. These reactions convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, a sugar molecule that serves as food for the plant. Oxygen is released as a byproduct of photosynthesis.
Light-Dependent Reactions, Process of photosynthesis graphic organizer
The light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. Chlorophyll molecules absorb sunlight, causing electrons to become excited and initiating the electron transport chain.
The electron transport chain pumps protons across the thylakoid membrane, creating a proton gradient. This gradient drives the synthesis of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), which are energy carriers used in the light-independent reactions.
Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
The light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle, occur in the stroma of chloroplasts. Carbon dioxide is fixed into organic molecules, primarily glucose, using the energy from ATP and NADPH generated in the light-dependent reactions.
The enzyme ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO) catalyzes the fixation of carbon dioxide. RuBisCO is regenerated through a series of reactions, ensuring the continuous operation of the Calvin cycle.
Environmental Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Environmental factors such as light intensity, temperature, and carbon dioxide concentration influence the rate of photosynthesis.
- Light intensity:Higher light intensity generally increases photosynthesis, up to a point where other factors become limiting.
- Temperature:Photosynthesis occurs optimally within a certain temperature range. Extreme temperatures can inhibit the process.
- Carbon dioxide concentration:Increased carbon dioxide concentration can enhance photosynthesis, especially in plants adapted to low CO2 environments.
Importance of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is crucial for life on Earth, providing:
- Food for plants and other organisms:Photosynthesis is the primary source of food for plants, which are consumed by herbivores and subsequently by carnivores.
- Oxygen production:Photosynthesis releases oxygen as a byproduct, which is essential for cellular respiration in all living organisms.
- Carbon cycle regulation:Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and incorporates it into organic matter, helping to regulate the Earth’s climate.
Quick FAQs
What is the primary role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll serves as the primary pigment responsible for absorbing light energy, initiating the process of photosynthesis.
How does the Calvin cycle contribute to photosynthesis?
The Calvin cycle, also known as the light-independent reactions, is responsible for fixing carbon dioxide into organic molecules, ultimately producing glucose.
What environmental factors can influence the rate of photosynthesis?
Light intensity, temperature, and carbon dioxide concentration are key environmental factors that can impact the rate of photosynthesis.
How does photosynthesis contribute to the global carbon cycle?
Photosynthesis plays a crucial role in regulating the levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, influencing the Earth’s climate.
What are some potential applications of photosynthesis in biotechnology?
Photosynthesis holds promise for applications in genetic engineering, biofuel production, and the development of artificial photosynthetic systems.